Ever wondered how we get seedless grapes or why some apples seem to stay fresh longer than others? It’s all thanks to the science of genetic tweaking to produce genetically modified foods (GM foods).
In recent years, prominent technological progress has occurred in the creation of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Some view the growth of GM foods as a manipulation of life, bringing forward concerns related to environmental and human health risks. Since GM foods continue to prevail in the global food sector, the challenges arising within the paradigm need to be addressed with appropriate food safety management measures.
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) refer to living entities—such as plants, animals, or microorganisms—whose genetic material (DNA) has been deliberately modified in a manner that does not occur naturally through traditional mating or natural recombination. Genetically modified foods (GM foods) are those that have had their DNA altered in order to boost crop protection, enhance flavor, or increase their ability to withstand tough weather.
Major Risks Associated with GM Foods
Potential dangers linked with the utilization of GM foods are identified in several domains.
Environmental Impacts
Compelling evidence suggests that GM plants can interact with their surroundings. The introduction of genes into these plants might result in the transfer of genetic material to other plants or organisms within the ecosystem. Pollen transport facilitates gene transfer, potentially leading to genetic contamination, especially among related plants. This could disadvantage natural wild plant varieties, potentially reducing or eliminating them due to competition with GM crops. Such shifts in biodiversity may lead to increased weed resistance, alterations in dominant species, and the decline or disappearance of others, causing widespread disturbances in ecosystems. Given these concerns, ongoing research is seen as imperative to more precisely evaluate the risks and advantages associated with GM crops.
Human Health Risks
There is a possibility of allergenic effects, particularly in individuals predisposed to allergies or other detrimental impacts on human health. Animal studies have highlighted weight gain, pancreas and kidney changes, immune system toxicity, and alterations in blood biochemistry, among other effects linked to GM products. The absence of comprehensive, long-term epidemiological studies raises skepticism among researchers about the safety of GM products, especially in terms of allergenic effects. Introducing a gene expressing a non-allergenic protein doesn’t guarantee a product devoid of allergenic action. Moreover, allergies triggered by GM products might be more potent and hazardous than those from conventional plants.
Antibiotic Resistance
Although the use of antibiotic-resistant genes has largely ceased in most modified products, the widespread utilization of antibiotics in animal feed remains a concern. This practice leads to antibiotics entering the human body through the consumption of meat and dairy products, fostering the development of resistant bacteria in the human digestive system. While antibiotic-resistant genes are not as prevalent in GM products now, further investigations are necessary to ascertain potential distinctions between transgenic and traditional plants and to gauge any additional risks GM plants might pose to consumers.
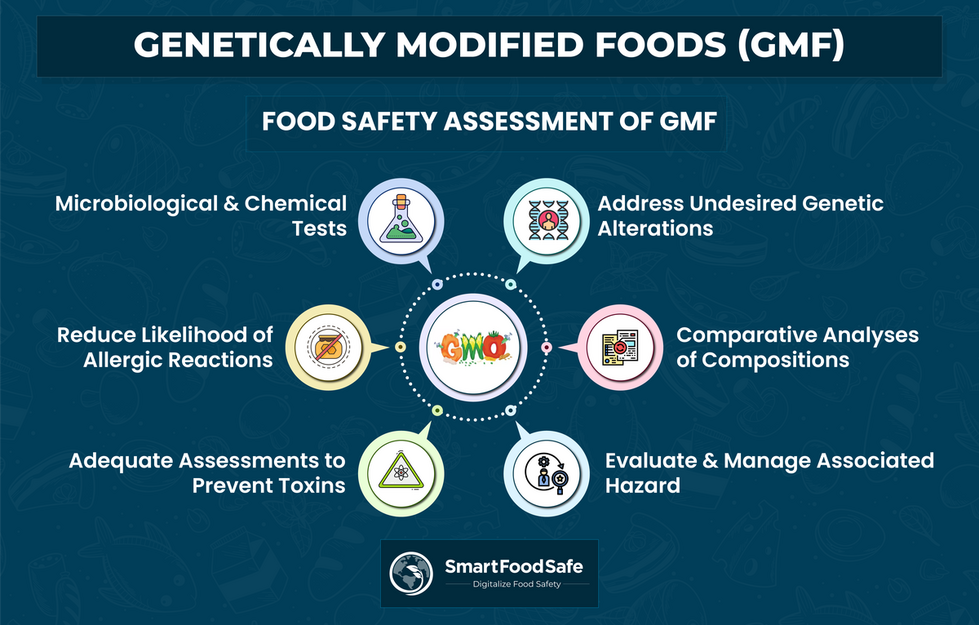
Managing food safety in the context of GM foods involves comprehensive strategies due to the complex nature of genetic modifications. Here are some food safety management strategies to be followed for GM foods:
Risk Assessment & Management: Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with GM foods. This involves evaluating the genetic modifications, potential allergenicity, toxicity, and unintended effects. Implement risk management strategies to mitigate identified risks.
Molecular Techniques & Genetic Analysis: Employ advanced molecular techniques to precisely analyze the genetic modifications in GM foods. This helps in understanding the specific alterations and potential impacts on allergenicity, toxicity, and nutritional content.
Toxicological & Allergenicity Assessment: Conduct toxicological studies and perform a detailed assessment of potential allergenicity by comparing the modified proteins in GM foods to known allergens. Advanced bioinformatics tools and protein analysis methods can aid in predicting and evaluating allergenic potential.
Monitoring & Surveillance Programs: Implement robust monitoring and surveillance programs to track GM foods in the market. This includes post-market surveillance to detect any adverse effects or unexpected changes in the food composition over time.
Traceability & Labeling: Develop traceability systems to accurately track GM ingredients throughout the supply chain. Clear labeling of GM foods allows consumers to make informed choices and also facilitates recalls if safety concerns arise.
Regulatory Compliance & International Standards: Adherence to stringent regulatory standards and compliance with international guidelines is crucial. Keeping updated with evolving regulations and standards ensures that GM foods meet the required safety criteria.
Public Awareness & Education: Educate consumers, stakeholders, and food industry professionals about GM foods, their safety evaluations, and the scientific basis for their approval. Transparent communication builds trust and confidence in the safety of these foods.
Continuous Research & Innovation: Invest in ongoing research to enhance methodologies for assessing the safety of GM foods. This involves staying updated with scientific advancements and adopting new technologies for more accurate assessments.
Collaboration & Information Sharing: Foster collaboration between regulatory agencies, researchers, industry experts, and international organizations to share data, insights, and best practices in GM food safety management.
Combining these methodologies in a systematic approach helps ensure the safety of GM foods, address potential risks, and maintain public confidence in their consumption.
Smart Food Safe’s digital modules for streamlined food safety and quality management are engineered to proactively identify and manage risks associated with food safety.
In today’s dynamic work environments, Smart Food Safe strives to excel in enabling real-time collaboration and data sharing across dispersed teams and operations. Leveraging a cloud-based quality management system (QMS), these modules offer a centralized platform that streamlines collaboration among diverse stakeholders, including teams, suppliers, and key stakeholders. This fosters efficient communication and coordination, essential for maintaining high-quality standards in food safety.
Furthermore, our software products can address the challenge of managing and storing substantial volumes of data generated from quality control processes, providing scalable and secure document storage.
_1.png)