Though often used interchangeably, did you know that purchasing and procurement are two distinct yet interdependent facets, critical to supplier management?
In essence, purchasing is a step within the larger framework of procurement. Procurement involves activities like sourcing, negotiation, and strategically selecting goods and services vital to an organization. On the other hand, purchasing specifically pertains to the act of placing orders for these goods and services. Organizations must delve deeper into these concepts and comprehend their core notions to fine-tune the processes and yield optimal business outcomes.
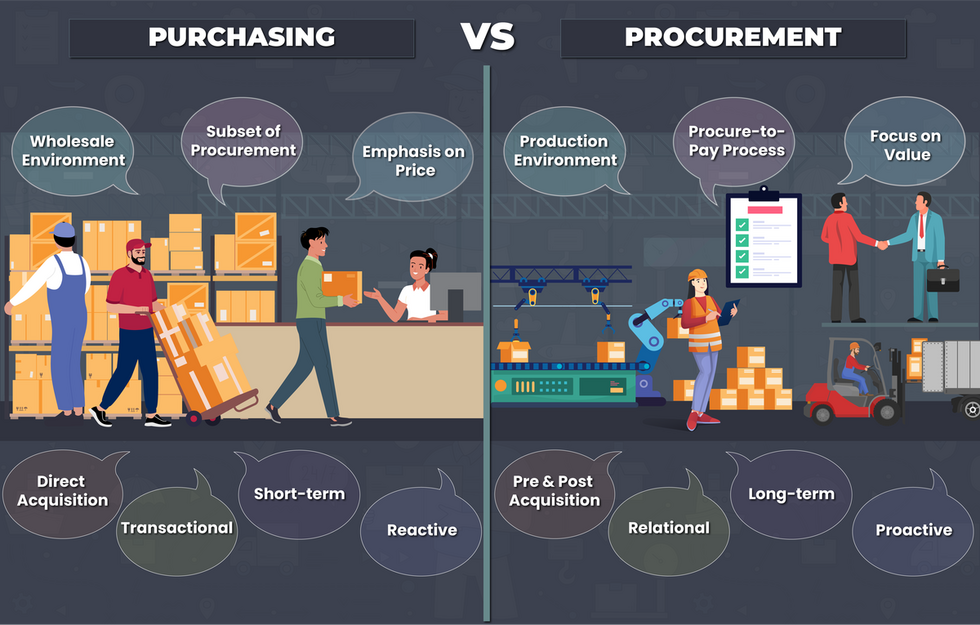
Purchasing encompasses the tasks involved in obtaining the necessary goods and services for an organization. It represents a subset of the larger procurement process, which entails a broader scope of functions.
Purchasing Lifecycle Overview
Generating a Purchase Requisition
Soliciting Proposals and Issuing Official Purchase Orders
Assessing the Quality of Received Products and Services
Verifying Supplier Documentation & Processing Payments
Maintaining Relevant Purchasing Records
What is Procurement?
Procurement involves the complete end-to-end process of acquiring goods, services, or works from external sources, covering everything from identifying needs to sourcing, negotiating, purchasing, receiving, inspecting goods, invoicing, making payments, and managing suppliers. The goal is to save costs, minimize time, and cultivate mutually beneficial relationships with suppliers.
Procurement Lifecycle Overview
Identifying Needs
Market Research
Supplier Evaluation and Selection
Negotiation
Contract Formation
Review and Control
In essence, when a company requires goods and services, you engage in both procurement and purchasing. However, these two activities diverge in their priorities and approaches toward achieving their respective objectives.
Short-term vs. Long-term: Purchasing typically focuses on short-term goals, such as obtaining goods or services quickly and efficiently at the best price. Procurement, on the other hand, has a more strategic, long-term perspective, considering factors like supplier relationships, sustainability, and risk management over time.
Transactional vs. Relational: Purchasing is often transactional, involving one-off transactions with suppliers to acquire goods or services. Procurement, however, is more relational, emphasizing ongoing partnerships with suppliers, collaboration, and mutual value creation.
Reactive vs. Proactive: Purchasing tends to be a reactive approach, responding to immediate needs or demands. In contrast, procurement takes a proactive approach by anticipating future needs, identifying potential risks, and strategically managing the supply chain to mitigate them.
Executing Transactions vs. Elaborate Procedures: Purchasing primarily involves activities such as ordering, expediting, and payment fulfillment, focusing on the execution of transactions. Procurement encompasses a broader range of activities, including need recognition (identifying organizational needs), sourcing (finding suitable suppliers), and contract closure (negotiating and finalizing agreements).
Direct Acquiring vs. Throughout Acquiring: Purchasing activities typically occur during the actual procurement process, from identifying the need to making the purchase and fulfilling the order. Procurement activities, however, encompass the entire lifecycle of acquiring goods or services, including pre-purchase planning, ongoing supplier management, and post-purchase evaluation.
Wholesale Environment vs. Production Environment: Purchasing often takes place in a wholesale environment, where goods or services are sourced externally from suppliers. Procurement can occur both externally (involving suppliers) and internally (managing the acquisition of goods or services within the organization’s production environment).
Emphasizing Price vs. Focus on Value: Purchasing may prioritize the price of goods or services, seeking the most cost-effective options. In contrast, procurement places greater emphasis on the value derived from these goods or services, considering factors such as quality, reliability, and long-term benefits rather than just initial costs.
Both procurement and purchasing are integral components of the procure-to-pay process, containing the steps involved in identifying and acquiring necessary goods and services. However, a robust supplier management strategy is imperative for optimizing purchasing and procurement through the following processes:
Supplier Selection and Evaluation: Careful assessment of potential suppliers based on criteria like quality, reliability, pricing, and capability ensures organizations align with their needs, directing procurement efforts towards reliable partners.
Relationship Building: Strengthening relationships through open communication and trust fosters collaboration, streamlines processes, negotiates favorable terms, and encourages suppliers to prioritize organizational needs for better service and support.
Contract Management: Efficient contract management ensures clear, enforceable agreements, minimizing risks, clarifying responsibilities, and preventing misunderstandings or disputes, ultimately optimizing procurement outcomes.
Performance Monitoring and Improvement: Continuous monitoring of supplier performance using KPIs allows organizations to identify areas for improvement, ensuring consistent meeting of expectations and driving continuous procurement process improvement.
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with supplier relationships, including supply chain disruptions and regulatory compliance issues, helps minimize disruptions and safeguard against potential losses or liabilities.
Technology Integration: Leveraging technology such as procurement software and data analytics tools streamlines tasks, reduces manual efforts, improves data accuracy, and provides insights for decision-making, optimizing purchasing and procurement activities.
Selecting between procurement and purchasing necessitates a nuanced evaluation, taking into account factors such as business size, industry, and specific requirements. Smaller enterprises with simpler operations may gravitate towards purchasing for its immediate and transactional nature, whereas larger corporations or those operating in industries with intricate supply chains stand to benefit from a holistic procurement approach offering long-term advantages and strategic alignment with business objectives.
Rather than a choice between procurement and purchasing, it is paramount to comprehend their distinct roles and facilitate their synergistic collaboration within the organization.
Smart Food Safe’s Smart Supplier is a contemporary vendor management software that enables the streamlining of purchasing and procurement procedures by digitalizing supplier qualification processes, supplier communication, and engagement, enhancing visibility into supplier performance, and automating repetitive supplier management tasks.
Smart Supplier provides an array of tools to elevate the supplier management efficiency in the procure-to-pay cycle with key features such as:
Supplier Lifecycle Management
Supplier Risk Assessment
Objective Vendor Qualification
Supplier Performance Evaluation
Supplier Portal
Alerts & Notifications
Non-compliance Management
Dashboard & Reporting
In conclusion, Smart Supplier empowers businesses to optimize their purchasing and procurement processes as part of their supplier management strategy, driving efficiency, cost savings, and strategic supplier relationships.
_1.png)