Did you know a research study on the global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis revealed an average of 93.8 million cases of gastroenteritis due to Salmonella species resulting in about 155,000 deaths occurring globally each year, out of which 80.3 million cases were foodborne?
Despite decades of extensive research on developing strategies to conquer Salmonella challenges, the persistent prevalence of Salmonella contamination in the food supply chain continues to be a pressing issue for food industries worldwide. The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) has introduced the Salmonella Grand Challenge, an extensive nationwide project that aligns and complements the sustained efforts of the Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) to enhance mechanisms in minimizing poultry-related human Salmonella illness.
Understanding Salmonella
Salmonella, a genus of gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family, comprises two species: Salmonella bongori and Salmonella enterica, with over 2500 serotypes identified to date. This resilient bacteria can survive for weeks in dry environments and months in water. The two most important serotypes causing transmission from animals to humans worldwide are Enteritidis and Typhimurium. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides key insights into Salmonella, as outlined below:
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an infectious illness primarily affecting the gastrointestinal tract, caused by the Salmonella bacteria. Symptoms include sudden fever, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, appearing within 6 to 72 hours after consuming contaminated substances. Most cases are mild and resolve within 2 to 7 days, but severe dehydration can be life-threatening, especially in vulnerable populations. Many salmonellosis cases go undiagnosed or occur sporadically, making identification challenging.
Sources & Transmission
Salmonella transmission occurs throughout the food chain, starting from animal feed to households and food-service establishments. Commonly found in the intestines of animals like poultry, livestock, and reptiles, it contaminates various food products, including fruits, vegetables, and water. Improper food handling and cross-contamination during preparation contribute to human infections. Person-to-person contact and contact with infected animals, including pets, can also lead to salmonellosis.
Difficulty in Eradicating Salmonella
Eradicating Salmonella poses significant challenges due to its diverse serotypes and unique characteristics. Its broad host range, including various animal species, hampers control efforts. The bacterium's ability to survive in low-moisture environments and tolerate harsh conditions, such as acidity and biofilm formation, adds to its resilience. Intensive production systems and vertical integration in the meat and poultry industries further complicate control measures. Moreover, antibiotic resistance has increased in Salmonella strains, reducing treatment options.
General Prevention Measures
Developing an effective Salmonella eradication strategy requires comprehensive data and predictive tools. Prevention measures should span from poultry production to consumption. Implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is crucial. Supplier control and raw material testing ensure the safety of ingredients, while employee training and hygiene practices reduce cross-contamination risks. Environmental monitoring and surveillance systems aid in early detection and response.
The Salmonella Grand Challenge was initiated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) as a collaborative research effort aimed at gaining a deeper understanding of how and where one of the greatest adversaries of food safety, Salmonella, poses the highest risk to meat and poultry products.
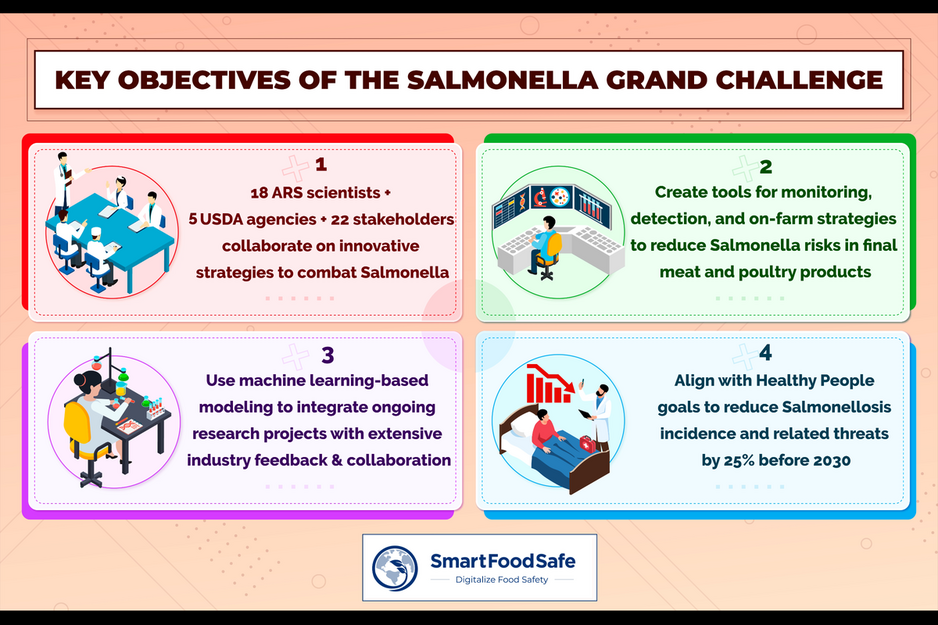
The team leading the Salmonella Grand Challenge comprises 18 scientists representing various fields of expertise and six national program areas within the Agricultural Research Service (ARS). These researchers are based in eight ARS research laboratories across the United States. It involves coordination with five U.S. Department of Agriculture agencies and 22 stakeholders from different commodities and scales of operation.
Highlights of the Salmonella Grand Challenge
It serves to streamline and optimize the USDA’s efforts in tackling the relentless problem of Salmonella by assembling a highly skilled team of scientists from diverse disciplines within the ARS to collaborate, synchronize their work, and devise ground-breaking approaches to fight against Salmonella.
The initiative intends to bring forth progressive monitoring and information tools for meat and poultry producers to prevent Salmonella-related issues within their operations effectively. These include optimizing detection and surveillance systems, building robust mitigation strategies, and promoting industry adoption of best practices against Salmonella.
The incorporation of ongoing research, standardization, and data harmonization is a crucial aspect of this endeavor, allowing the identification of overarching trends, emerging threats, and novel strategies to mitigate Salmonella.
The Grand Challenge also aligns with the Healthy People goals, aiming to reduce the incidence of salmonellosis and its associated health risks by 25% before 2030, an objective in line with the goal of improving public health and food safety.
Progress & Future Implications
Machine learning-based modeling techniques can be expected to be utilized in producing state-of-the-art models that encompass on-farm strategies along with the trans-disciplinary approach presented by the Grand Challenge to derive data from various research projects, industry feedback, advancing genomics, data analytics, and biosecurity measures for eliminating Salmonella risks in meat and poultry products.
As the Grand Challenge initiative gains momentum, maintaining a long-term commitment to tackling Salmonella contamination is crucial. In conclusion, with the support of various stakeholders and a commitment to continuous research and joint efforts, the initiative holds promise for reducing the incidence of Salmonella and ensuring a safer food supply chain.
With the mission to revolutionize quality and food safety management through intelligent software solutions, Smart Food Safe works toward delivering digital modules capable of assisting food businesses secure public health by preventing pathogenic food illnesses originating from food production operations. Smart EMP provides a comprehensive system that digitalizes any environment monitoring program, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis of the food production environment, detecting potential sources of contamination, and allowing timely corrective actions in case of non-compliance. Food industries can enforce an efficient food safety management system (FSMS) with Smart HACCP through systematic risk assessment and proactive remediation measures to digitally manage the identification and implementation of critical control points throughout food processing.
_1.png)