A game-changing approach of incorporating Quick Response (QR) codes on food product labels to improve the inclusivity of conveying food safety information to all consumers, especially those with visual impairments, was brought about by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
Under the Food Safety and Standards (Labeling and Display) Regulations, 2020, the FSSAI has already established comprehensive guidelines for the information to be included on food product labels. The primary purpose of these regulations is to empower consumers with fundamental information about the food they buy to make informed decisions when selecting food products.
The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act 2016 provides that “the appropriate Government shall ensure that the PWD enjoy the right to equality, life with dignity, and respect for his or her own integrity equally with others.” As a result, in line with these principles, the FSSAI seeks to augment the dissemination of food product data for visually disabled persons with the aid of QR codes on food labels, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their special needs, can access safe and nutritious food.
What are QR codes? How do they work?
A Quick Response (QR) code is a form of barcode that digital devices can effortlessly scan, encoding data as a grid of pixels within a square shape.
QR codes work by encoding information in a two-dimensional matrix of black squares on a white background. These codes can store various data types, such as URLs, text, or contact information. When a QR code is scanned using a compatible device, like a smartphone camera, the encoded data is extracted and processed. The device’s software interprets the pattern of squares to reveal the information, allowing quick and convenient access to websites, information, or other digital content without the need for manual data entry.
QR codes in the Food Industry
QR codes are commonly employed for tracking product information within supply chains, as well as being a prevalent feature in marketing and advertising initiatives. QR codes have proven to be a versatile tool in the food industry, offering a convenient way to access information, enhance transparency, and boost customer engagement while adapting to the evolving needs and preferences of consumers. Here are some ways in which QR codes are applied currently in the food sector:
Menu Access: Many restaurants and eateries use QR codes on their tables or printed menus. Customers can scan the code with their smartphones to access the menu online, reducing the need for physical menus and minimizing contact during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Food Traceability: QR codes can leverage consumers with information about the origin and journey of their food products. Customers can scan a QR code on a product’s packaging to learn about its source, production methods, and safety checks, building trust and confidence in the food supply chain.
Nutritional & Allergen Data: QR codes can link to detailed allergen information and nutritional data for each menu item or food product. This is especially useful for consumers with dietary restrictions or allergies who must make careful food choices.
Food Safety and Recall Information: In case of food recalls or safety alerts, QR codes can quickly inform consumers about the issue and provide instructions on returning or disposing of affected products.
Customer Engagement: QR codes can be made part of marketing and loyalty programs, enabling customers to scan codes for discounts and promotions or to participate in surveys, providing valuable feedback to the food business.
Recipe Suggestions: QR codes can provide recipe ideas or cooking instructions for food products. For example, a QR code on a bag of pasta can link to a website with various pasta recipes, encouraging consumers to purchase the product.
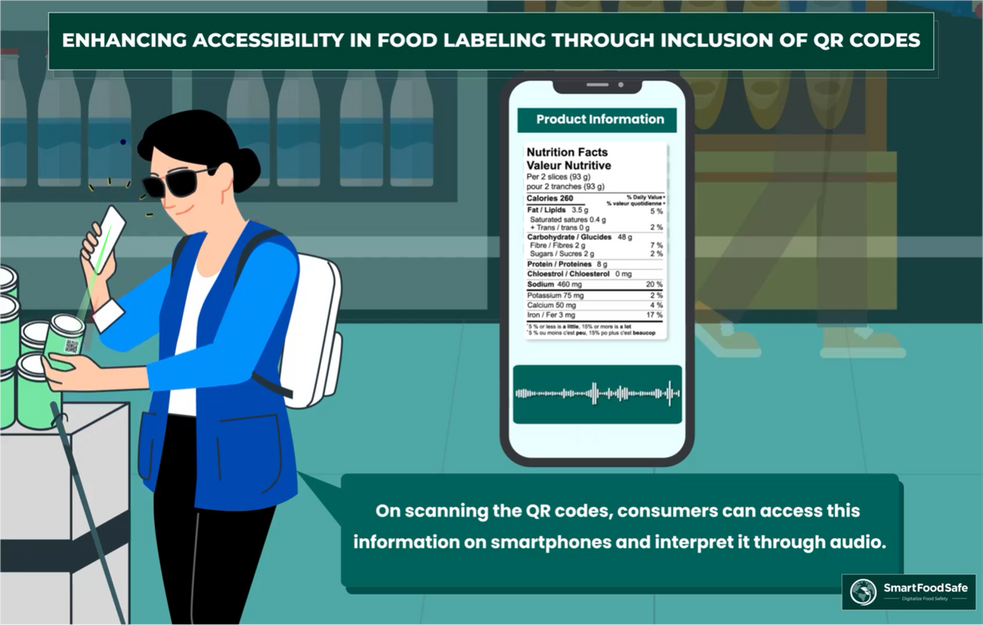
All customers are entitled to know exactly about the food they purchase, ascertaining that they receive precisely what was guaranteed and advertised to them. Since food labels demonstrate information about food visually, it becomes a constraint for consumers having visual disabilities to fathom and exercise their rights. QR codes on food labels simply facilitate this process.
According to FSSAI ’s advice, Food Business Operators (FBO) should include QR codes as part of a mandate for front-of-pack (FOP) warning labels and contain extensive information about the product, comprising of but not limited to ingredients, nutritional information, allergens, manufacturing date best before/expiry/use by date, allergen warning, and contact information for customer inquiries. This complements the efforts to educate consumers in a tech-assisted way, significantly enabling visually disabled people to perceive this vital information to elevate their awareness to make healthy food choices.
However, using the QR code does not replace or negate the requirement to provide mandatory information on the product label, as prescribed by relevant regulations, but optimizes the availability of the same information to those incapable of accessing and utilizing it.
Smart Food Safe aims to lead the way in supporting food companies to remain at the forefront of the industry by offering cutting-edge software modules equipped with the latest trends in the food supply chain. One such digital solution that eases the label management process is Smart Label, a Nutritional Fact and Labeling Management Software.
Smart Label streamlines and centralizes the creation of precise, regulatory-compliant nutritional labels for food products by harnessing an elaborate ingredient database. This allows food manufacturers, processors, and distributors to effortlessly determine nutrition facts, allergens, and other critical label details. The platform offers an intuitive interface for label design, ingredient data import, and change tracking, all while automating the cumbersome process of updating labels to reflect ingredient modifications or regulatory changes. With features like automatic recipe analysis, label generation, and multi-language support, Smart Label simplifies regulatory compliance with diverse and emerging industry requirements, such as adapting QR code technology in food labels, ultimately saving time and resources while ensuring the safety and integrity of food products.
_1.png)